House of Saud
House of Saud is the ruling royal family of Saudi Arabia.
The monarchy was hereditary by a version of agnatic seniority until 2006, when a royal decree announced that future Saudi kings are to be elected by a committee of Saudi princes. Even prior to this, the king would select and assign his own heir apparent (rather than that automatically being the eldest of his sons) and that person would serve as crown prince of the kingdom and ascend the throne upon the death of the king.
The current ruler of Saudi Arabia is King Salman (born 1935), who ascended the throne in 2015 after the death of his half-brother King Abdullah.
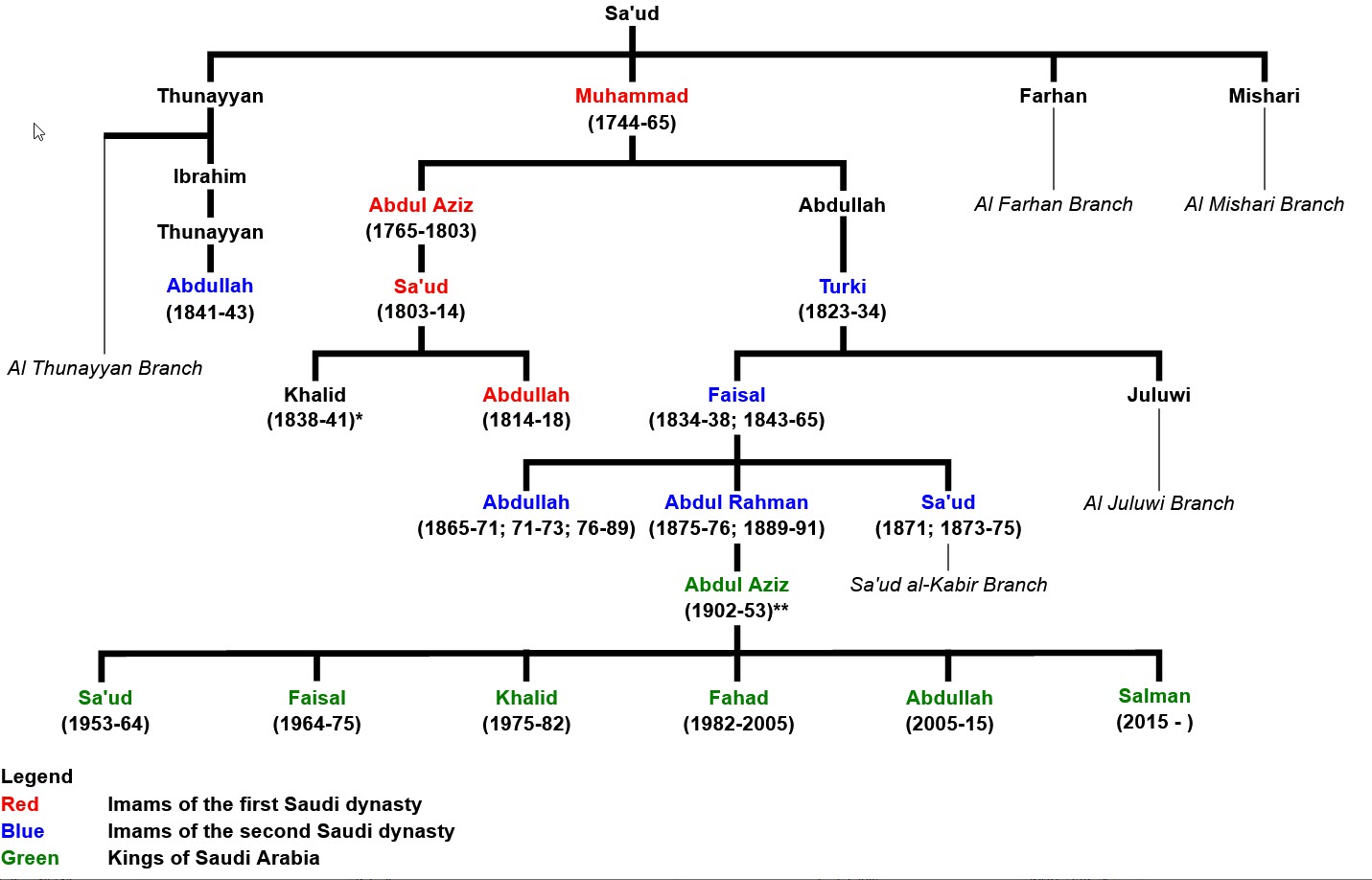
The founding father of the Saudi dynasty was Muhammad bin Saud, who established the Emirate of Diriyah in 1744. The currently ruling fraction of the house is primarily led by direct descendants of Abdulaziz bin Abdul Rahman Al Saud (Ibn Saud), who established the present kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
The House of Saud contains approximately 15,000 individuals, but most of the power and wealth is concentrated within a group of circa 2,000 people. All members of the royal family have the title Emir. Only sons, daughters, patrilineal granddaughters and grandsons of Kings are referred to by the style “His/Her Royal Highness” (HRH). Patrilineal great-grandsons and members of cadet branches are only “His/Her Highness” (HH).
The king´s formal title is His Majesty The King of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia and
Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques.
Milestones for the House of Saudi
- Establishment of the first Saudi state in 1744
The first Saudi State, known as the Emirate of Diriyah, lasted from 1744 to 1818, and was characterized by expansive Salafism.
- Establishment of the second Saudi state in 1824
The second Saudi State, known as the Emirate of Nejd, lasted from 1824 to 1891, and was characterized by a lot of internal conflict within the emirate.
- Establishment of the Emirate of Riyadh in 1902 and the Unification in 1932, i.e. the establishment of the third Saudi state.
Through a series of conquest from 1902 and onward, Abdulaziz bin Abdul Rahman Al Saud (Ibn Saud) established the third Saudi State, and it evolved into the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia in 1932.
Political power
The head of the House of Saud is also the King of Saudi Arabia and the Head of State of Saudi Arabia. Saudi Arabia is an absolute monarchy. The king is the one who appoints ministers to his cabinet, and these ministers supervise their respective ministries.
For the Ministry of Defence, Ministry of Foreign Affairs, and Ministry of the Interior, it is very usual to appoint anyone as minister who is not a member of the Saud family. They same is true for the thirteen regional governorships, and for critical military and governmental departmental posts.
When it comes to portfolios, the situation is different, and it is actual common to give portfolios (e.g. Finance portfolio, Labour portfolio, Petroleum Affairs portfolio, and Industry portfolio) to Saudi citizens who are not members of the House of Saud. With that said, junior Al Saud member will typically serve as deputies. For portfolios that have extra large budgets, younger close relatives are typically appointed as either deputies or vice minister. One example is Prince Abdul Rahman, the sixteenth son of King Abdulaziz, who served as vice minister of defence and aviation under defence minister Prince Sultan.
